Understanding The Normal Balance of an Account
Understanding this difference is crucial for all financial analysis. Let’s see in detail what these fundamental rules are and how they work when a business entity maintains and updates its accounting records under a double entry system of accounting. Knowing what a normal balance gives you the basics of double-entry bookkeeping. It’s not that difficult to figure out to what account type each transaction belongs to.
Identifying Normal Balances Across Account Types
So, anything that increases the Owner’s Equity will also have a credit normal balance. At the same time, anything that reduces this account will have normal debit balances. Revenue accounts show money made from business activities and have a credit balance. This means increases in revenue boost equity through credits.
Defining Normal Balance of Accounts
- He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com.
- Instead, it signifies whether an increase in a particular account is recorded as a debit or a credit.
- When we’re talking about Normal Balances for Revenue accounts, we assign a Normal Balance based on the effect on Equity.
- When we’re talking about Normal Balances for Expense accounts, we assign a Normal Balance based on the effect on Equity.
- Keep in mind, the fix might require just a simple edit or a more complex journal adjustment.
- Costs that are matched with revenues on the income statement.
The key to understanding how accounting works is to understand the concept of Normal Balances. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. A counter account is an account that is linked to another account and regulates its balance.
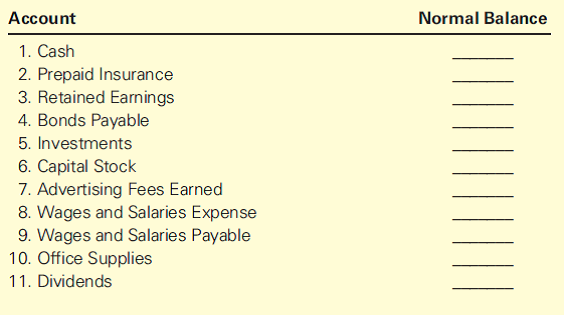
Normal Balance of Accounts
Ensuring the accuracy of account balances is a continuous process that involves meticulous examination and reconciliation. Accountants must regularly scrutinize ledger entries to confirm that each transaction adheres to the principles of double-entry bookkeeping and reflects the correct normal balance. This scrutiny often involves comparing ledger balances with independent external sources, such as bank statements, to validate the accuracy of recorded transactions. Discrepancies between these sources can reveal errors or omissions that require correction.
This expectation serves as a checkpoint for accountants, who can quickly verify whether an account’s balance aligns with its normal state or if further investigation is warranted. Equity accounts represent the owner’s interest in the company. This includes contributed capital, retained earnings, and in some cases, drawings or dividends.
What are Closing Entries in Accounting? Accounting Student Guide
In practice, the term debit is denoted by “Dr” and the term credit is denoted by “Cr”. In the rest of this discussion, we shall use the terms debit and credit rather than left and right. This is a non-operating or “other” item resulting from the sale of an asset (other than inventory) for more than the amount shown in the company’s accounting records. The gain is the difference between the proceeds from the sale and the carrying amount shown on the company’s books. Sales are reported in the accounting period in which title to the merchandise was transferred from the seller to the buyer. This way, the transactions are organized by the date on which they occurred, providing a clear timeline of the company’s financial activities.

For example, if a Liability account has a debit balance, then it is necessary to check if no errors were made in the bookkeeping records. The normal balance of an account is not just a static feature; it is dynamically influenced by the business’s transactions. As the business environment evolves and transactions occur, the balances in these accounts will fluctuate. However, the fundamental expectation of whether an account should have a debit or credit balance remains unchanged.
Retained earnings reflect a company’s total profits after dividends. They show a credit normal balance for retained earnings because they are part of equity. Looking at assets from most to least liquid tells a company its risk. Using ratios from the balance sheet, like debt-to-equity, helps compare a company’s health to others.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur or a seasoned business owner, understanding the normal balance of accounts is crucial to keeping your business’s financial health in check. There is an easy way to remember normal balance accounting definition which accounts should be increased on a debit side and which ones on credit – using the balance sheet equation. How will this help to determine the normal balance of a particular account?
By recording transactions as debits or credits correctly, companies ensure their financial reports are accurate. It also helps meet rules set by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and the IRS. Another misconception is that normal balances are the expected ending balances for accounts. In reality, normal balances indicate the side of the ledger that increases the account. For instance, while expenses have a normal debit balance, it is not expected that these accounts will always have a debit balance at the end of a period. Expenses are periodically closed to equity, which can result in a temporary zero balance.
He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. We will apply these rules and practice some more when we get to the actual recording process in later lessons. An allowance granted to a customer who had purchased merchandise with a pricing error or other problem not involving the return of goods.